News Release
5/19/2025
NORITAKE CO., LIMITED
Noritake Diamond-Nickel Heat Dissipation Substrate Achieved a High Thermal Conductivity of 1200 W/(m・K)
NORITAKE CO., LIMITED (Headquarters: Nagoya, Aichi; Representative Director and President: Akira Higashiyama; hereinafter referred to as “Noritake”) announces the development of a diamond-nickel heat dissipation substrate*1 with high thermal conductivity*2 for semiconductor applications in high-speed communications (5G, 6G). This substrate can efficiently dissipate heat, helping prevent performance degradation and device failure. Noritake has achieved a thermal conductivity of 1200 W/(m·K).
Market Environment
High-speed communication standards such as 5G are increasingly being adopted, enabling the transmission and reception of high-speed, large-capacity data. This technology enhances the convenience and efficiency of various communication services. As a result, base stations and data centers are increasingly using communication devices*3 employing next-generation semiconductors that can transmit large volumes of data.
However, as communications speeds and data capacities increase, the amount of heat generated by semiconductors also rises. In order to ensure stable operation and extend the lifespan of semiconductors, there is a growing need for heat dissipation substrates with high thermal conductivity to quickly and efficiently release heat.
In manufacturing heat dissipation substrates for semiconductors, a large substrate is cut into multiple smaller substrates. Increasing the substrate size improves productivity and helps reduce manufacturing costs.
Challenges in Using Diamond as a Heat Dissipation Substrate Material

Diamond, with its high thermal conductivity (1000–2000 W/(m·K)), is well-suited for quick dissipation of large amounts of heat and is considered a promising material for heat dissipation substrates. However, synthesizing diamond into large substrate sizes requires significant manufacturing costs and long production time. There is a growing need for technologies that can leverage diamond’s excellent thermal conductivity while enabling larger substrate sizes.
Features of “Diamond-Nickel Heat Dissipation Substrate” with High Thermal Conductivity
Noritake succeeded in producing heat dissipation substrates that fulfill the needs of size and high thermal conductivity. Noritake applied its plating technology,*4 which was cultivated through the production of grinding tools to densely bond diamond particles with nickel.
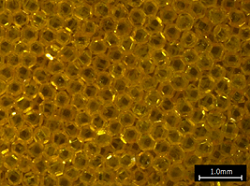
① High Thermal Conductivity of 1200 W/(m·K)
Through a “high-density single-layer arrangement,” Noritake has maximized the thermal conductivity of diamond. The thermal resistance when heat passes through the bonding material, nickel (70 W/(m·K)), was minimized.
② Successful Development of 100 mm × 100 mm Substrate Prototype
With its unique plating technology, Noritake succeeded in producing heat dissipation substrates that fulfill the needs of size and high thermal conductivity.
Comparison Between Noritake Product and Competitor’s Products
(Heat Dissipation Substrates Made of Diamond)
<Results of In-House Tests>

*1 A substrate used to efficiently dissipate heat from heat-generating components, such as semiconductors.
*2 A material property that indicates how easily heat can be transferred. The larger the value is, the more easily heat can be transmitted.
*3 A device primarily used on computers to send and receive data.
*4 A processing technology that forms a thin metal film on the surface of metals or non-metals.









