News Release
11/18/2025
NORITAKE CO., LIMITED
Noritake Develops PFAS Removal System Using Fine Bubbles
- Achieves Over 99% Removal of High-Concentration PFAS -
NORITAKE CO., LIMITED (Headquarters: Nagoya, Aichi; Representative Director and President: Akira Higashiyama) has developed a new PFAS removal system that uses fine bubbles*1, enabling the removal of more than 99% of PFAS*2 from liquids. The system also helps significantly reduce CO₂ emissions generated during the thermal decomposition process following PFAS removal.
■Market Environment
PFAS are chemicals known for their excellent heat resistance, water and oil repellency, and chemical stability. They have been widely used in applications such as food packaging, cookware, and firefighting foams. Among them, PFOS*3 and PFOA*4 are representative substances that have been extensively utilized. However, since they hardly degrade in nature and persist for long periods, concerns have been raised about their impact on human health and ecosystems.
■Challenges in PFAS Removal
Adsorption using activated carbon is a widely used method for removing PFAS (PFOS, PFOA). Under this method, the activated carbon must be incinerated after adsorption to thermally decompose PFAS, making the carbon non-reusable. Since activated carbon is carbon-based, the incineration process results in substantial CO₂ emissions. Consequently, development of technologies that reduce the amount of activated carbon incinerated is also underway.
■Features of the Newly Developed System

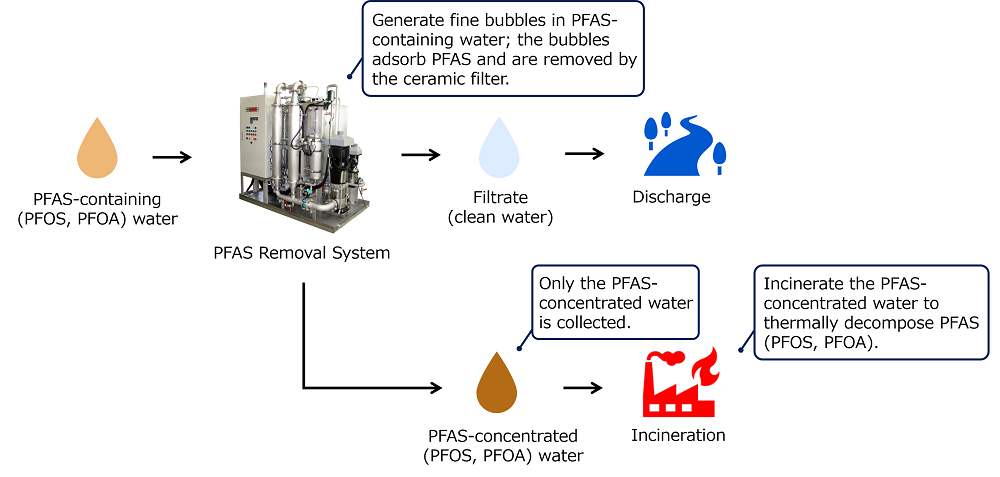
Noritake has developed a PFAS removal system consisting of a fine-bubble generator and a ceramic filter, both utilizing ceramic technologies. This system generates fine bubbles in PFAS-containing water, adsorbs PFAS (PFOS, PFOA), and removes them using a ceramic filter.
① Over 99% Removal of High-Concentration PFAS
The system is capable of removing more than 99% of high-concentration PFAS (PFOS, PFOA) up to approximately 1 mg/L.
② Reduces CO₂ Emissions by Approximately 90%
Only the PFAS-concentrated water collected by the ceramic filter is incinerated, significantly reducing CO₂ emissions during the thermal decomposition process of PFAS-containing water.
③Reusable Components
Both the fine-bubble generator and ceramic filter use ceramic materials which are regenerable ceramic materials, enabling repeated use and lowering long-term running costs.
■Mechanism of PFAS Removal Using the Developed System
■Glossary
*1 Fine bubbles: Bubbles with a diameter of less than 100 μm.
*2 PFAS: Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, consisting primarily of carbon and fluorine.
*3 PFOS: Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid.
*4 PFOA: Perfluorooctanoic acid.
Contact Information
NORITAKE CO., LIMITED Engineering Group Fluid Technology Dept.
E-mail:mixing@noritake.com









